Main Content
The Qualifications Framework in Swiss Higher Education
A qualifications framework systematically describes the qualifications generated by a country’s educational system. This description includes the general profile that holders of a respective qualification have; the competencies and skills developed for the qualification in question; and reference to the formal aspects of the respective educational level.
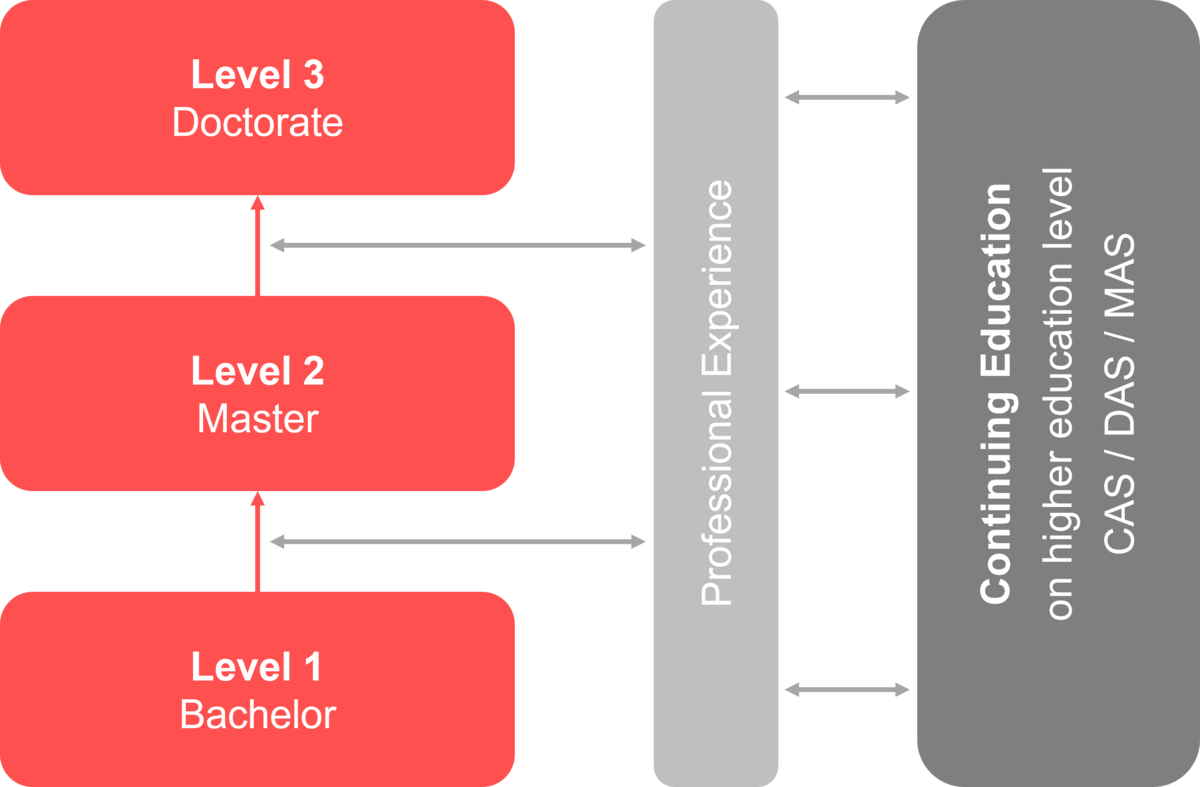
The Swiss higher education framework (nqf.ch-HS) comprises the three-cycle educational system Bachelor – Master – Doctorate. It makes Swiss higher educational qualifications more easily comparable in a European and international context.
Besides the nqf.ch-HS, the Swiss educational system utilizes a second sectorial qualifications framework: the NQR Vocational Education for those qualifications developed in vocational education.
At European level, the nqf.ch-HS is compatible with the Qualifications Framework for the European Higher Education Area (QF-EHEA). In accordance with the EQF recommendation, bachelor's degrees are classified at level 6, master's degrees at level 7 and doctoral degrees at level 8 of the European Qualifications Framework (EQF).
Purpose of a Qualifications Framework
The main purpose of a national qualifications framework is to enable the comparative assessment of the competencies acquired throughout the various degrees of the national education system in an international context. It constitutes the foundation for the international recognition of degrees. When developing their degree programs, Swiss higher education institutes are therefore guided by the descriptors of the Swiss qualifications framework.
Profiles of the Educational Paths
The many decrees issued by sponsors and coordinators as well as higher education policy resolutions of the federal government and cantons make the common benchmarks of the Swiss qualifications framework indispensable.
Universities
Universities focus on theory- and research-based scientific education. The Master's degree is the standard qualification.
Universities of Applied Sciences
Universities of applied sciences focus on practical, occupationally-qualifying education, which requires students to apply scientific knowledge and methods as well as creative and artistic skills, depending on the subject area. Usually, a Bachelor’s degree qualifies a graduate for a profession.
Graduates of the second-level degree of universities of applied sciences can attain a doctoral degree through cooperative partnerships with universities.
Universities of Teacher Education
As science-based professional schools, universities of teacher education focus on the training of teachers and pedagogical professionals for all levels. The third level of study (doctorate), which qualifies students to independently develop scientific findings, is offered by universities and other institutions of the higher education sector.
Graduates of the second-level degree of universities of teacher education can attain a doctoral degree through cooperative partnerships with universities.
Continuing Education in Higher Education
With their continuing education offerings, higher education institutions support individuals who are already working in a professional environment to gain further qualifications. Compared to other providers in the continuing education market, higher education continuing education distinguishes itself by its self-conception as part of higher education and its positioning within the academic system, while simultaneously orienting itself toward practical application.